I want you to forget what you thought you knew about carbs and fats, and focus on the fuel! Today, I will introduce you to how fuel is different, and how your fuel intake can affect your thyroid, weight gain, and other issues you might be facing. Without further ado, let’s make sense of the best fuel for you.
- Have any questions?
- 480-631-7837
- support@in-goodhealth.com

Whole Grains – Who Should Eat And Who Should Avoid?
May 7, 2018
Are Oxalates To Blame For Inflammation In Your Body?
June 4, 2018
Whole Grains – Who Should Eat And Who Should Avoid?
May 7, 2018
Are Oxalates To Blame For Inflammation In Your Body?
June 4, 2018Product Recommendation: RS Complete benefits GI health through its ability to support microbial balance and proper intestinal permeability and integrity. Additionally, this formula may help support optimal blood sugar and insulin levels, appetite control, and cardiovascular health. Click Here

Fuel: Defined
To start, I really want to dive deep and uncover more about the concept of fuel itself – and how it relates back to your body and your health. While we have talked a lot about whether carbohydrates or fats are more important, but to your body, they are really not that different (at a molecular level).
The truth is that they all break down into something known as oxaloacetate. This even applies to ketones, too. For that reason, they are all treated and considered as fuel for the body.
If your body has too much fuel, it has to find a place to store the excess amounts. On the opposite side, when you have too little fuel you will typically pull it out of those “excess stores” and burn it as needed.
There are times where your body may not be able to process fuel as well as it should. I will dive into that a bit later, though.
Bottom Line: Due to the basic molecular makeup of carbs, fats, and even ketones, we can consider all of these to be fuel for your body. What we do with that fuel, and how we process it, is what really matters when it comes to our overall health and energy.
Types of Fuel

Just like most things in life, fuel is all about balance. That means that there are definitely good versions and bad versions of fuel, so I want to break down each of them for you…
Key Insight: When it comes to your intake of fuel, it is not only important to get good versions of each type of fuel, but to get a good total of each.
Carbohydrates
The primary thing that carbs bring to the table are:
- Resistant Starch
- Fibers
- Polyphenols
- Phytonutrients (like those found in intact whole grains)
The drawback is that those carbohydrates which are higher in fructose can be more difficult for the body to effectively process.
Fats
The good thing about fats is that they can provide us with essential fats. Such as:
- The omega-3s, and
- The omega-6s
The drawbacks come from the other types of fats that we might also ingest. There are trans fats, which are harmful, and saturated fats, which are harmful in certain amounts (but harmless at smaller levels).
Ketones
There are two types of ketones that I want to hone on in, which are:
- Endogenous ketones (those we make)
- Exogenous (those we can ingest)
When it comes to those that we can ingest, we can get those from purified ketones like gamma-hydroxybutyrate or some from medium-chain triglycerides.
The thing that I want you to know is that we can certainly consider ketones as a fuel. This means that if your body has more than it needs, you can still turn ketones into fat. If there is less fuel total than you need, ketones are unable to make it work differently in any way.
Alcohol
In order to really round out these types of fuels, I do need to mention alcohol. Alcohol is a compound that we can burn as fuel, but there is really no clear positive involved.
While there might have been some previous research about alcohol and cardiovascular health, these research studies are now in dispute.
In terms of negatives, alcohol has been linked to:
- Cancer risk
- Brain aging
- Liver disease
While it does act like a fuel, alcohol certainly works differently when compared to carbs, fats, and ketones. It really does not carry the same positives at all.
Your Health, Your Fuel Intake

Based upon your goals, and what you want to achieve with your fuel intake, I want to dive a bit deeper into how much fuel (and what types of fuel) might be best for you…
Thyroid Health
If you are looking to improve your thyroid function, a mixture is ideal. What you will want to have is a mix of proteins, good fats, good carbs, and you will want your body to make some ketones, on occasion, as well.
Key Insight: Ketones can be produced during periods of intense exercise, as well as during an overnight fast.
You will also want to make sure that you are getting lots of fibers, as well as resistant starch, healthy proteins, and essential fatty acids.
Bottom Line: Interested in learning more about the different ways that you can improve what you are eating, and how it can help benefit your overall health? Please take some time today to see my collection of beneficial products to help your thyroid perform (Thyroid Supplements).
Weight
If your main goal is body weight, this next point is going to be so important for you to hear: There is no such thing as one magic fuel and no such thing as one evil fuel.
Why do I say this? Well, all of the large studies that have looked at low-carbohydrate versus low-fat versus ketogenic diets have all proved that there is no advantage – the only advantage is recognizing your total fuel intake, and abiding by that concept.

Once you look at the total, it does not matter how you rearrange them, because it really makes no difference. Studies have tracked people, some as far as two years out, looking at:
- Mixed diets
- Low-fat diets
- Low-carb diets
While there might be the odd individual who might seem to do better on one of these diets, versus another, but there is never a group difference. This means that for everyone one person who does better on a low-carb diet, we have another who might be better on low-fat – or a group of folks who would be fine no matter which way they went.
Bottom Line: If you take away anything from today’s article, I really want you to know that it is the fuel total that matters for your body and weight loss journey.
Athletic Performance
If you are talking less about competitive activities, where you might require high bursts of strength or activity, it may not make a large difference. You can probably burn fat for fuel, and still maintain good endurance the remainder of the way.
When it comes to high levels of competition, though, you need to keep some things in mind. If you need high bursts of strength for up to a few seconds at a time, then there is an advantage to having glycogen.1
Glycogen, as we understand it, comes only from carbohydrates. This means that for competitive performances, carbs do have the ability to help. But it only applies in the context of all the other nutrients, since you still need:
- Essential fats, and
- Protein for proper recovery
Bottom Line: When it comes to physical activity, and physical activity that is not competitive or requiring large bursts of strength, your fuel intake will be less strict as you will be able to burn fuel while maintaining good endurance along the way.
Brain Aging
There is lots of talk about how ketones and fats can play an important role in reversing brain aging. The data has not shown this to be the case, though. Instead, the best approach to combating brain aging is to have a nice mix of all those fuels.
Another important thing to note is that while ketones might be good, they can reach a point where they are counterproductive. Think of it like this: your brain uses ketones as a building block, and the more you are forced to burn them as a fuel the less you have them in your brain as a building block.
This means that your brain shifts to burning them, and gets to the point where they can no longer rebuild with ketones. Paradoxically, ketones are good, but there is a sweet spot that we need to abide by to ensure our brain’s overall health.
Bottom Line: I have talked about recent discussions around saturated fats and brain aging recently, and I would love for you to find out more to get to the heart of this issue (Read: Are saturated fats good for your brain).
Fuel By Risk
As opposed to your end goal, what if you need to focus on fuel for risk? Here are some of the common risks, and how you can figure fuel into the equation…
APOE Gene
The APOE gene controls how your body circulates cholesterol and fats (The apoe gene and a new study about it). If you have what is known as a 3 or 4 variation, you are going to be apt to have more risks from diets that are higher in fat. This is a case where you are far better off to be lower in fat, higher in carbs, while still getting essential fats and quality protein.
Bottom Line: If your genotype is anything besides that variation, you have more options and it probably does not make as big of a difference for you.
Lipid Panels
If your lipid panel runs really high in triglycerides, then you are someone who might be more sensitive to overall carbohydrate and processed carbohydrate. This means that you are better off having:
- Moderate amounts of carbs
- Healthy amounts of polyunsaturated (and monounsaturated) fats
- Good quality proteins
Also worth noting is that if you run really high in LDL cholesterol, you may be more sensitive to total fat intake. At that point, you would really want to reduce overall saturated fat and focus hard on healthy amounts of fibers in your diet.
Glucose Metabolism
Glucose metabolism, blood sugar, is also important to consider. As it happens, any type of fuel can result in your body being fuel-resistant. For example, if you have high blood sugar and you consume the same amount of fuel, but you shifted away from carbohydrates and toward fats, what will happen is that your blood sugar will get better.
But, and this is key, your triglycerides will get higher! You can take another step and suggest that you put yourself in a ketogenic state, where you are burning ketones, and that high level of circulating ketones is a circulating fuel.
Glucose, ketones, triglycerides, all of these are types of fuel that your body is not equipped to deal with, so they are either being left in the blood or leaving your body via your urine.
Imagine a collection of airplanes trying to land at your local airport, but there is absolutely no room on the runway. Instead, the planes just stay up in the area (and they do not land). This is what happens when you have high glucose, high triglycerides, and high ketones in the blood or urine (it is fuel with nowhere to go).
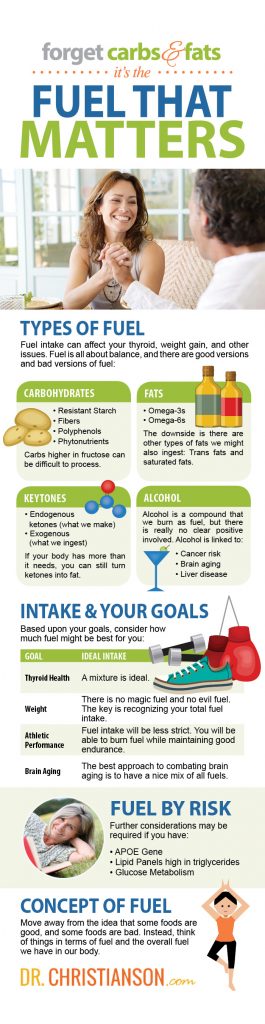
Your Concept of Fuel
I hope from our conversation today that I have helped you move away from this idea that some foods are good, and some foods are bad. Instead, we need to think of things in terms of fuel – both the kinds of fuel and the overall fuel we have in our body.
This more collective concept of “fuel load” is important to your body, and so is the health of your thyroid. Do you feel like you really have the full picture of your own health? I would love for you to learn a little bit more, which is why I would suggest taking the Thyroid Quiz (Click Here) today.
1 – https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/02640414.2011.585473

P.S. Whenever you are ready, here is how I can help you now:
- Schedule a Thyroid Second Opinion with me, Dr. C, Click Here for Details
- Need help to choose supplements? Click ‘Help Me Decide Here'
- Get my top books Here
Dr. Alan Glen Christianson (Dr. C) is a Naturopathic Endocrinologist and the author of The NY Times bestselling Hormone Healing Cookbook, The Metabolism Reset Diet, and The Thyroid Reset Diet.
Dr. C’s gift for figuring out what works has helped hundreds of thousands reverse thyroid disease, heal their adrenals, and lose weight naturally. Learn more about the surprising story that started his quest.